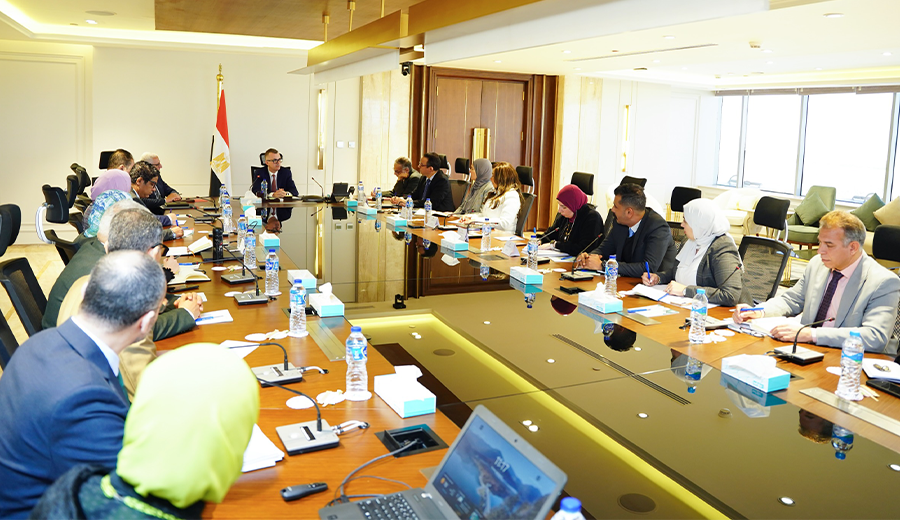
During a Meeting Between H.E. the Minister of Planning, Economic Development, and International Cooperation and the Planning and Budget Committee in the House of Representatives to Present Key Indicators of the Egyptian Economy

29 December 2024
H.E. Dr. Rania Al-Mashat: Restructuring economic authorities to improve efficiency and increase their contribution to the GDP is a priority for the government.
Dr. Hussein Issa: A study on the status of 59 economic authorities, with 6 possible scenarios for their restructuring.
H.E. Dr. Rania Al-Mashat, Minister of Planning, Economic
Development, and International Cooperation, affirmed that restructuring
economic authorities to improve efficiency and increase their contribution to
the GDP is a top priority for the government. She explained that the Supreme
Committee for Economic Authorities was established in 2022, followed by the
formation of a technical committee chaired by Dr. Hussein Issa to assess the
conditions of these authorities and explore optimal options for each, with the
goal of benefiting the national economy.
This came during a broad meeting she held today with the
Planning and Budget Committee in the House of Representatives. The meeting
aimed to discuss the actual implementation of the 2023/2024 fiscal year’s
economic and social development plan, review the economic situation, and assess
the status of economic authorities. The meeting was chaired by H.E. Dr. Fakhry
El-Feki, Chairman of the Planning and Budget Committee, with the attendance of
the honorable members of parliament.
For his part, Dr. Hussein Issa, Chairman of the Technical
Secretariat of the Committee for the Reform and Restructuring of Economic
Authorities, explained that the technical secretariat was formed in June 2024 by
a decision of H.E. Prime Minister Dr. Mustafa Madbouly. The committee has held
several meetings in partnership with the Ministries of Planning, Economic
Development, and International Cooperation, and Finance, to study the economic
authorities. To date, 59 files have been prepared concerning various
authorities across the country, containing both financial and non-financial
data. This is the first phase, which aims to categorize each authority
according to six alternatives: either retaining the authority, converting it
into a public authority, merging some authorities, splitting an authority into
smaller entities, liquidating and dissolving the authority, or transforming it
into a holding company. He further explained that after completing the first
phase, the results will be presented to the Supreme Committee chaired by the
Prime Minister for a decision before moving into the second phase, which will
involve separate plans and work arrangements.
During her participation, H.E. Dr. Rania Al-Mashat reviewed
the efforts to implement the structural reform program. She highlighted the
state’s commitment to achieving comprehensive and sustainable development
through the coordinated efforts of various institutions, according to
integrated strategic plans. The Ministry of Planning, Economic Development, and
International Cooperation is responsible for monitoring the implementation of
Egypt’s Vision 2030 and the national economic and structural reform program.
This is done in coordination with all relevant ministries and agencies and in
cooperation with international development partners to secure financing for
budget support that will assist in implementing structural reforms aimed at
enhancing economic competitiveness, improving the business environment,
bolstering the macroeconomy’s resilience to external shocks, supporting the
green transition, and opening future prospects for comprehensive and
sustainable development, all to maximize the benefits of financial and
technical development partnerships.
H.E. Dr. Al-Mashat also discussed the main pillars of
economic and structural reform policies, which include enhancing macroeconomic
stability, diversifying the production structure of the Egyptian economy by
focusing on the real economy sectors such as industry, agriculture, and
information and communication technology, increasing competitiveness, improving
the business environment, supporting the transition to a green economy,
enhancing labor market efficiency and flexibility, and developing vocational
education and training systems.